Ren W, Liu S, Zhang H, et al. Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer International Publishing, 2016: 154-169.
1. Overview
现有的hand-designed feature
- dark channel
- color disparity
- maximum contrast
- fusion schemes
存在局限性。因此,论文提出multi-scale结构
- coarse-scale net. predict holistic transmission map
- fine-scale net. refine result locally
1.1. 模型

网络使用max-pooling增加模型的非线性能力,而输出的t需要与hazy image尺寸一样,因此使用bilinear interpolation.
网络预测透射率矩阵t. 选择t中0.1%透射率最小的像素点位置,对应到hazy image像素点,其中强度最大的值作为A
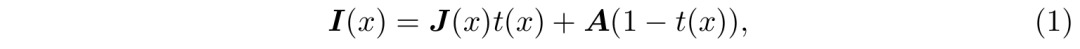
当t为0时,对其设置阈值

1.2. Loss Function

同时用在coarse-scale和fine-scale的网络输出上.
1.3. 数据集
- A = [k, k, k], k ∈ [0.7, 1.0]
β ∈ [0.5, 1.5]
β ∈ (0, 0.5),透射率增大,导致thin haze, boost noise
- β ∈ (1.5, OO), 透射率减小
- 利用数据集提供的depth-meta生成数据.
320 x 240
NYU Depth Dataset
- Training Set. 6000 images x 3
- Middlebury Stereo Dataset
- Valid Set. 50 images x 3
1.4. Related Work
- Multiple images
- Albedo
- Maximizing local contrast
- Boundary constraint and contextual regularization
- Dark channel prior
- Random Forest
2. Experiments
2.1. 实验结果

He.估计的透射矩阵是均匀分布的,一些区域中的hazy thickness overestimated.

2.2. 运行时间

2.3. 泛化性
虽然real image depth通常很大,而训练集中的depth较小。但是可以通过调整介质的消光系数(medium extinction coefficient)来增加雾的浓度。这种方案独立于depth,能够包含real transmission map的范围。
2.4. Fine-Scale的作用
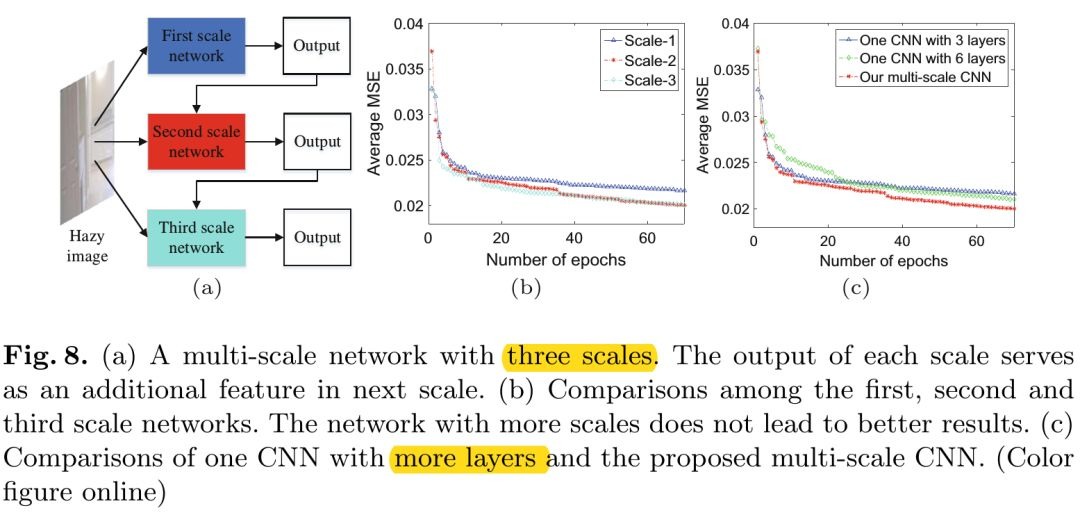
- 3-scale网络性能并没有提升
- single-deep-scale网络性能降低
得出结论:相比于high-level task,deep structure对low-level task并不明显。
2.5. Up-Sampling的作用

- (c)不使用pooling,效果较差
- 虽然(d)与(b)相似,但(b)计算量较大
2.6. 特征提取方法对比

CNN提取的特征类似于dark channel, local max contrast.
2.7. Failure Case

由于缺少相应数据,对夜间hazy image效果并不好
2.8. Future Work
- 处理上述缺陷
- End-to-end同时估计transmission map, atmosphere light