Keyword [Universal Adversarial Perturbations]
Akhtar N, Liu J, Mian A. Defense against universal adversarial perturbations[C]Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018: 3389-3398.
1. Overview
In this paper, it proposed the first framework to defend against universal adversarial perturbation
- learn a Perturbation Rectifying Network (PRN) as pre-input layers
- perturbation detector trained on the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)
1.1. Contribution
- PRN
- methods to compute synthetic image-agnostic perturbations to train PRN
- separate perturbation detector learned from DCT
1.2. Related Work
- FGSM
- DeepFool (iterative)
- adversarial transformation network
- ensemble
- foveation
- distillation
- JPG compression
- SafetyNet. detect and reject adversarial example
1.3. Problem Formulation

- I_c. clean image
- ρ. perturbation
- δ. fooling ratio (set 0.8)
- ξ. 2000 for l_2, 10 for l_oo
- detector

rectifier

I_{ρ/c}. perturbation image or clean image
2. Methods
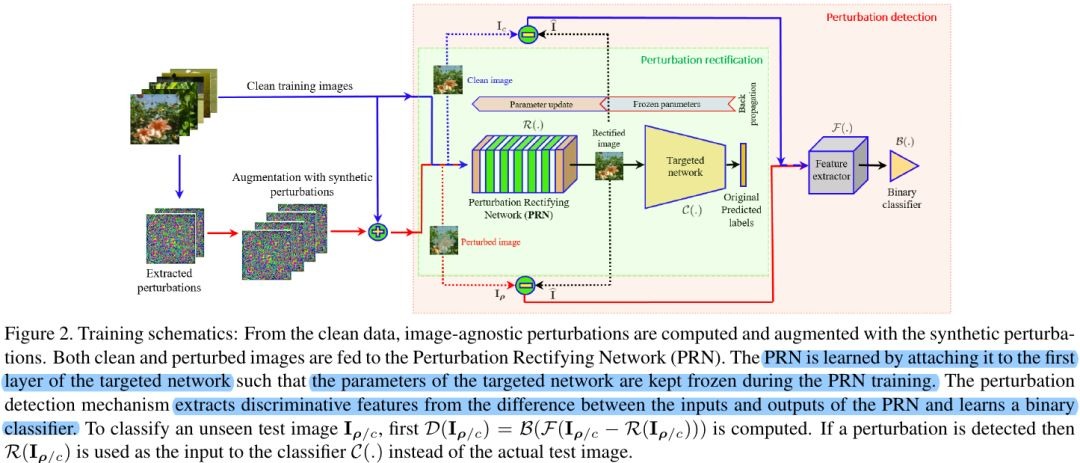
2.1. PRN

- Θ. weights
- b. bias
- l*. predicted by joint network
- l. predicted by target network
- implemented as 5-ResNet blocks
- cross entropy loss
- Adam with momentum (0.9, 0.999)
- LR 0.01 decay by 10% eack 1K iteration
- batch size 64
2.2. Synthetic Perturbation Generation


- fooling ratios for the synthetic perturbation is lower than the original ones but in an acceptable range
- help in early convergence and better performance of the PRN
2.3. Perturbation Detection
- DCT based compression can also be exploited to reduce the network fooling ratio under the universal perturbation
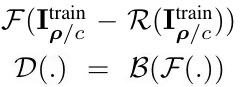
- B. SVM
- F. compute log-absolute values of the 2D-DCT coefficients of the gray-scaled image
if detect perturbation
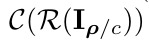
else
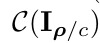
3. Experiments
3.1. Metric

3.2. Results


